by Kappy Prasad | Feb 9, 2015 | Articles, Blog, Linux, Technical
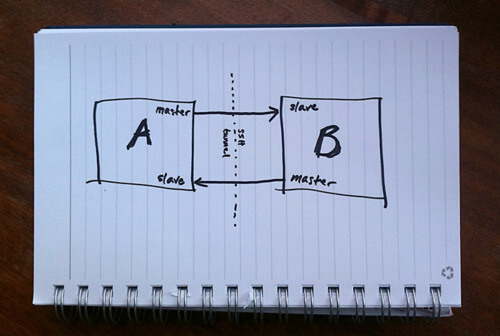
MySQL Replication is incredibly simple to get up and running and this post will instruct you through it. Simple Master -> Slave Replication MySQL allows you to build up complex replication hierarchies, such as multi-master, chains of read slaves, backup databases at a remote site or any combination of these. This article focuses on a simple single master to single slave setup. This article also assumes that 2 MySQL Servers have been installed but that there is no existing data in the master that needs to be copied to the slave – it’s not complex to add that extra requirement and it will be covered in a future post. Server “masterhost” (192.168.0.31) is to be our master and “slavehost” (192.168.0.34) the slave. Step 1: Edit the configuration files & start the MySQL Servers The first step in setting up replication involves editing the “my.cnf” file on the servers that will serve as the master and slave. A default is provided with the MySQL installation but in case there is already a production MySQL database running on these servers, we provide local configuration files “master.cnf” and “slave.cnf” that will be used when starting up the MySQL servers. At a minimum we’ll want to add two options to the [mysqld] section of the master.cnf file: log-bin: in this example we choose inodecloud-bin.log server-id: in this example we choose 1. The server cannot act as a replication master unless binary logging is enabled. The server_id variable must be a positive integer value between 1 to 2^32 master.cnf: [mysqld] server-id=1 log-bin=black-bin.log datadir=/home/inode/mysql/master/data innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1 sync_binlog=1 Note: For the greatest possible durability and consistency in...

by Kappy Prasad | Jan 21, 2015 | Articles, Blog, Linux, Technical
If you’re a developer or work in IT, you’ve likely heard of Docker. It’s a 3 year old open source technology that has grown exponentially during its existence. And now, it’s beginning to turn heads in even the most regulated industries. First let’s explore what Docker actually is for those that are unfamiliar. “Docker is an open platform for developers and sysadmins to build, ship, and run distributed applications,” according to the Docker website. The technology consists of two tools, the Docker Engine and the Docker Hub. The Docker Engine is a, “portable, lightweight runtime and packaging tool,” while Docker Hub is a, “cloud service for sharing applications and automating workflows.” The technology is particularly appealing for developers because it is now easier than ever to make sure you develop, test and deploy using the same environment as your colleagues, resulting in less issues caused by differences or missing libraries. Docker also offers developers the flexibility to quickly run their apps anywhere, whether its on laptops, VMs or QA servers. More simply put, “Docker helps developers build and ship higher-quality applications, faster.” Sysadmins are finding the technology useful as well, because of the ability to standardize development environments among other reasons. “Docker helps sysadmins deploy and run any app on any infrastructure, quickly and reliably.” Docker seems to be on the same disruption path as GitHUB, which shook the source control systems, or more lately, how composer “revolutionized” the way we deploy components of a PHP and Symfony application. On the business side, the benefits may be huge. By simplifying the way we deploy apps and creating more manageable...

by Kappy Prasad | Jan 19, 2015 | Articles, How To's, Linux, Technical, Wordpress
With WordPress powering 61% of CMS based websites, it has become a lucrative target for hackers. Google blacklisting for phishing and email blacklisting for spamming is quite common in WordPress hosting. A well maintained WordPress site is immune to hacking, but in shared hosting, the majority of WordPress websites will be un-patched, and vulnerable to hacking. Through a few simple strategies, it is possible to make WordPress immune to hacking. Securing the web server through web application firewalls The efficiency of a web application firewall largely depends on how quickly the firewall is able to include zero day WordPress exploits into their signature database. While commercial signatures gave close to 100% detection rates, free rules from Comodo, AtomiCorp, etc for the mod_security Apache module is good enough to prevent more than 95% of exploit attempts. Additionally, we were able to extend the malware detection capability of mod_security module by integrating it with ClamAV anti-virus software. Enabling auto-upgrade for WordPress installations Since WordPress v3.7, automatic security updates are switched on by default, and wouldn’t break anyone’s site. We further extended this feature by plugins like Advanced Automatic Updates, which can upgrade plugins and themes as well. For customers who chose security over extensive customization, the full-auto-upgrade worked very well in preventing website exploits. File upload scanning through FTP Compromised FTP accounts are another major source of malware uploads. Desktops, laptops and mobile devices get infected with trojans all the time, and web masters losing their FTP login details are a common cause of malware uploads. We put a block on this channel by deploying file upload scanners. For those web hosts...

by Kappy Prasad | Jul 16, 2014 | Linux, Technical
What is GitHub? Git is an open-source version control system very similar to other version control systems such as Subversion, CVS and Mercurial. What is it used for? When developers are coding, they are making constant changes to the code and releasing new version. Version control systems keep these revisions & store the modifications in a cloud repository allowing developers to easily collaborate, as they can download a new version of what they are building, make changes, and upload the newest revision. Every developer can see these new changes, download them, and contribute. Features in GitHub Let me go over a few of the basic features in GitHub to give you a basic understanding of what each feature is and what it is used for. Repository A Repository is where all the files for a particular project are stored and provided by a unique link. Forking In GitHub you have the ability to grab another Git members project and create a new project , modifying the code and creating your own version or adding in new features Pull Request A Pull request is used for when you want copy the files however any changes will be notified to the original developer where they can choose to accept the changes or not. Compare Compare shows a list of all the commits unique to a branch, the sum of all the files changed across all of those commits, and a unified difference of all of those changes. It clearly summarizes what the branch represents. Basic Git Commands git clone this command is used to upload your local directory files to your Git Project. git status Used to show files that have not been...
by Kappy Prasad | Jul 10, 2014 | Linux, Technical
When you ask most people how do you transfer or migrate your site over the common answer is “oh i use Filezilla and download to my local drive then upload to the new directory”. This is not really the easiest way to migrate but a two step process of downloading the uploading, what if you had to transfer lets say a 200Gb site over. This was the case with our partner Mindarc who is a Digital Agency that looks after some high profile Ecommerce Websites and their client A Learning Place who is hosted on our cloud. Me being lazy and looking for the easiest way to do something i suggest using this command line to do a DIRECT Site to Site transfer just from terminal from Mac or Linux or use Putty if you are using Windows. Open up a terminal and enter this: scp -rp SSHUSERNAME@IP:<DIRECTORY OF SOURCE> SSHUSERNAME@IP:<DIRECTORY OF DESTINATION> Now lets dissect and see what the heck this means. SCP – Secure copy is a means of securely transferring computer files between a local host and a remote host or between two remote hosts -r parameter – known as recursive, sometimes we need to copy the directory of all the files inside. -p parameter – Provides modification times, access times, and modes from original files The first SSHUSERNAME@IP:<DIRECTORY OF SOURCE> is the SSH connection username and where the originating files are located so for example it would be something like this: root@192.168.1.23:/var/www/public_html/ The second section is where is the remote server where the files are going and which directory will it be placed under, for example: root@102.203.122.124:/var/www/user/html/website/ So the complete command looks something like...






